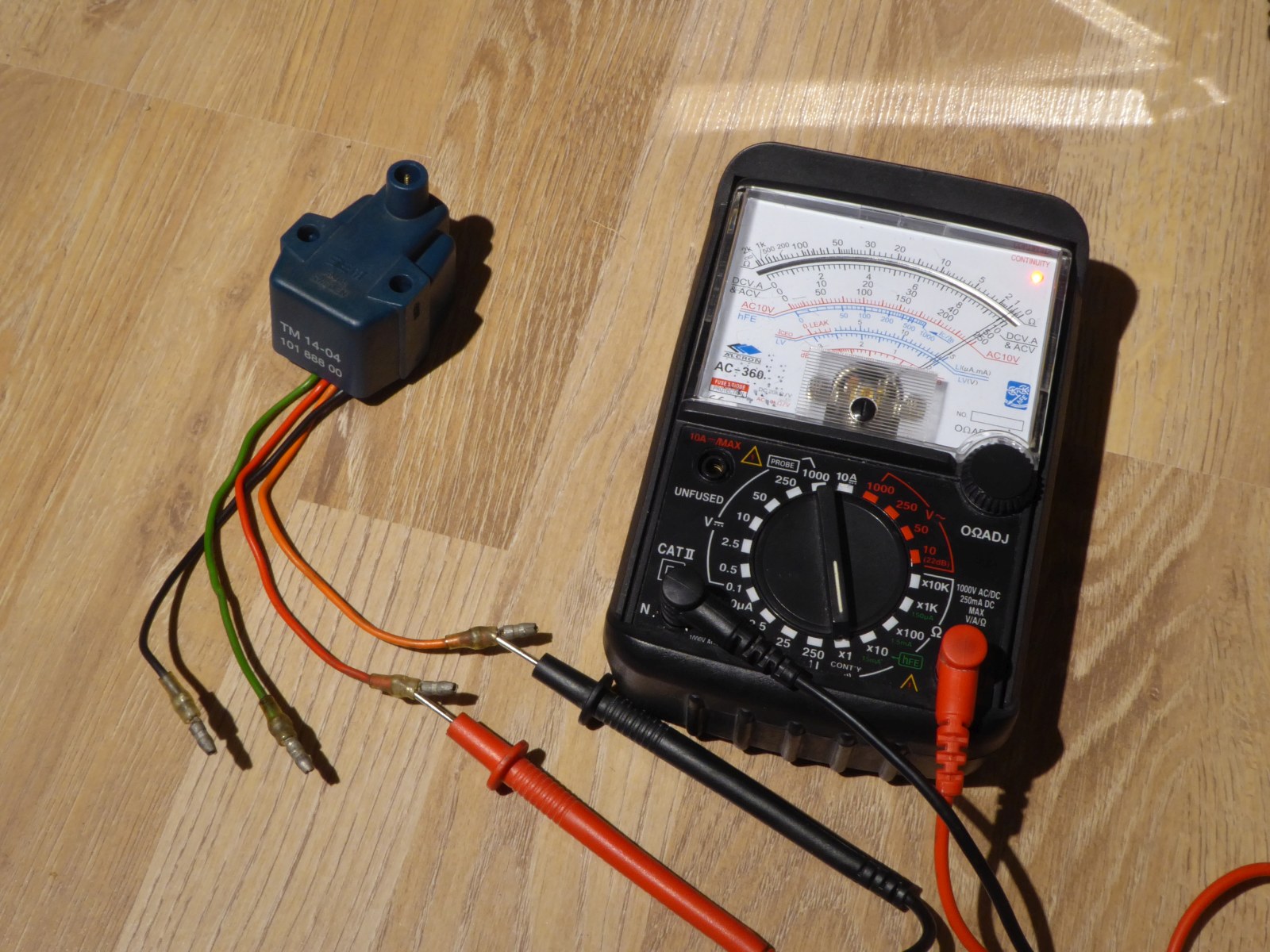
How to test ignition coil with multimeter

The ignition coil is an important component in a vehicle's ignition system. It plays a crucial role in generating the high voltage needed to ignite the fuel in the engine cylinders. However, like any other part, the ignition coil can experience issues over time. Some common problems include misfires, stalling, and rough idling. These symptoms can be indicative of a faulty ignition coil, although they may also be caused by other issues. In order to accurately diagnose the problem, it is necessary to test the ignition coil using a multimeter.
- What is an Ignition Coil?
- Signs of a Faulty Ignition Coil
- Tools and Materials Needed
- Safety Precautions
-
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Ignition Coil with Multimeter
- Step 1: Park the Vehicle in a Safe and Well-Ventilated Area
- Step 2: Disconnect the Battery
- Step 3: Locate the Ignition Coil
- Step 4: Remove the Ignition Coil
- Step 5: Set Up the Multimeter
- Step 6: Test Primary Ignition Coil Circuit
- Step 7: Test Secondary Ignition Coil Circuit
- Step 8: Analyze the Multimeter Readings
- Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References
What is an Ignition Coil?
An ignition coil is a vital part of a vehicle's ignition system. Its purpose is to convert the low voltage from the battery into the high voltage needed to create a spark at the spark plugs. The ignition coil works through a process of electromagnetic induction. It consists of primary and secondary windings, and a core made of ferrous material. When current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field then induces a high voltage in the secondary winding, which is transferred to the spark plugs.
Components of an Ignition Coil
An ignition coil is made up of several components, each with a specific role:
- Primary winding: This is the low voltage winding of the ignition coil. It consists of a few hundred turns of wire and is connected to the vehicle's battery.
- Secondary winding: This is the high voltage winding of the ignition coil. It consists of several thousand turns of fine wire and is connected to the spark plugs.
- Core: The core is made of a ferrous material, such as iron or steel. It helps to concentrate the magnetic field generated by the primary winding.
- Distributor: In older ignition systems, the distributor is responsible for distributing the high voltage from the ignition coil to the correct spark plug. In newer systems, this function is performed by an ignition control module or coil packs.

Signs of a Faulty Ignition Coil
When an ignition coil starts to fail, it can exhibit a range of symptoms. Here are some common signs that may indicate a faulty ignition coil:
- Misfires: If the ignition coil is not providing enough voltage to the spark plugs, the engine may misfire or run rough.
- Stalling: A faulty ignition coil can cause the engine to stall, especially during acceleration or at high speeds.
- Rough idling: The engine may run unevenly or have a rough idle if the ignition coil is not functioning properly.
- Loss of power: A weak or failing ignition coil can lead to a loss of power, making it difficult to accelerate or climb hills.
It is important to note that these symptoms may also be caused by other issues, such as a faulty fuel injector or a clogged air filter. Therefore, it is crucial to thoroughly test the ignition coil before replacing it.
Tools and Materials Needed
In order to test the ignition coil with a multimeter, you will need the following tools and materials:
- Multimeter: This is the key tool for testing the ignition coil. It should have the ability to measure both resistance and voltage.
- Safety goggles: It is important to wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from sparks or other hazards.
- Gloves: Gloves can help protect your hands when working with electrical components.
Safety Precautions
Working with electrical components can be dangerous, so it is important to take the necessary safety precautions. Here are some steps you should take:
- Wear safety goggles: Safety goggles will help protect your eyes from sparks or other potential hazards.
- Wear gloves: Gloves can help protect your hands from electrical shocks or burns.
- Disconnect the battery: Before starting any testing procedures, it is crucial to disconnect the vehicle's battery to prevent accidental electrical contact.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Ignition Coil with Multimeter
Step 1: Park the Vehicle in a Safe and Well-Ventilated Area
Before you start testing the ignition coil, make sure to park the vehicle on a level surface in a safe and well-ventilated area. This will ensure that you have enough space to work and that there is proper air circulation.
Step 2: Disconnect the Battery
Prior to any testing, it is essential to disconnect the battery to prevent any electrical accidents. Follow these steps to disconnect the battery:
- Locate the vehicle's battery, which is usually found under the hood or in the trunk.
- Using a wrench, loosen the nut on the negative terminal (marked with a minus sign) of the battery.
- Slide the connector off the negative terminal of the battery and move it away from the battery.
This will ensure that there is no electrical power running through the vehicle while you perform the tests.
Step 3: Locate the Ignition Coil
Depending on the vehicle, the ignition coil may be located near the engine or on the firewall. Consult your vehicle's manual to locate the ignition coil. In most cases, it will be connected to the spark plugs by a series of wires.
Step 4: Remove the Ignition Coil
Before you can test the ignition coil, you will need to remove it from the vehicle. The process may vary depending on the type of ignition coil your vehicle has:
- Coil-on-plug ignition system: In this type of system, each spark plug has its own ignition coil. To remove the ignition coil, you will need to disconnect the electrical connector and remove any securing bolts or clips. Once removed, the ignition coil can be easily pulled out.
- Coil pack ignition system: In this type of system, all the ignition coils are housed together in a single unit called a coil pack. To remove the coil pack, you will need to locate and remove any securing bolts or clips. Once removed, you can unplug the electrical connector and carefully lift out the coil pack.
Be sure to handle the ignition coil with care to avoid any damage.
Step 5: Set Up the Multimeter
Before you can start testing the ignition coil, you will need to set up the multimeter. Follow these steps:
- Turn on the multimeter and select the resistance (ohms) setting.
- Depending on your multimeter, there may be a range of resistance settings. Choose the appropriate range for the expected resistance of the ignition coil. Consult your vehicle's manual or do some research to find the expected resistance value.
For example, if the expected resistance value is in the range of 0.3-1.0 ohms, you would select the corresponding range on the multimeter.
Step 6: Test Primary Ignition Coil Circuit
The primary circuit of the ignition coil consists of the primary winding and the wiring that connects it to the battery. Follow these steps to test the primary circuit:
- Connect the multimeter to the ignition coil's positive and negative terminals. Make sure the connectors are securely attached.
- Read the resistance value on the multimeter. Compare it to the expected resistance value. If the measured resistance is significantly higher or lower than the expected value, the ignition coil may be faulty.
Step 7: Test Secondary Ignition Coil Circuit
The secondary circuit of the ignition coil consists of the secondary winding and the wiring that connects it to the spark plugs. Follow these steps to test the secondary circuit:
- Disconnect the ignition coil wires from the spark plugs.
- Connect the multimeter's positive lead to one of the ignition coil wires and the negative lead to the other wire.
- Read the resistance value on the multimeter. Compare it to the expected resistance value. If the measured resistance is significantly higher or lower than the expected value, the ignition coil may be faulty.
Step 8: Analyze the Multimeter Readings
After testing both the primary and secondary circuits, you will have obtained resistance readings from the multimeter. Here are some guidelines to help you interpret the results:
- If the resistance values are within the expected range, the ignition coil is likely functioning properly.
- If the resistance values are significantly higher or lower than the expected range, the ignition coil may be faulty and will need to be replaced.
- If the resistance values are inconsistent or fluctuating, you may have a loose connection or a faulty multimeter. Double-check all connections and consider using a different multimeter for more accurate readings.
It is also important to note that the specific resistance values will vary depending on the vehicle's make and model. Refer to your vehicle's manual or consult a reliable source to determine the correct values for your ignition coil.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Issue 1: Low or No Resistance in Primary Circuit
If the multimeter reading shows low or no resistance in the primary circuit, it could indicate a problem. Possible causes include a faulty ignition control module or wiring issues. Here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Inspect the wiring connections to ensure they are secure and not damaged.
- If the wiring appears to be in good condition, the ignition control module may be faulty and will need to be replaced.
Issue 2: High Resistance in Primary Circuit
If the multimeter reading shows high resistance in the primary circuit, it could indicate a problem. This can be caused by a damaged ignition coil or corroded connectors. Here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Inspect the ignition coil for any visible damage, such as cracks or burns. If damage is found, the ignition coil will need to be replaced.
- Check the connectors for any signs of corrosion. If corrosion is present, clean the connectors using a suitable electrical contact cleaner.
- If the ignition coil and connectors appear to be in good condition, the issue may be with the wiring. Inspect the wiring for any damage or loose connections. Repair or replace any damaged wiring as necessary.
Issue 3: Low or No Voltage Output in Secondary Circuit
If the multimeter reading shows low or no voltage output in the secondary circuit, it could indicate a problem. Possible causes include a damaged ignition coil or faulty spark plugs. Here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Inspect the ignition coil for any visible damage, such as cracks or burns. If damage is found, the ignition coil will need to be replaced.
- Check the spark plugs for signs of wear or damage. If the spark plugs are worn or faulty, replace them.
- If the ignition coil and spark plugs appear to be in good condition, the issue may be with the wiring. Inspect the wiring for any damage or loose connections. Repair or replace any damaged wiring as necessary.
Issue 4: Inconsistent or Fluctuating Readings
If the multimeter readings are inconsistent or fluctuating, it could indicate a problem with the connections or the multimeter. Here are some troubleshooting steps you can take:
- Check all connections, including the multimeter probes and the ignition coil terminals, to ensure they are secure and making good contact.
- If the connections appear to be secure, try using a different multimeter to see if the issue persists. A faulty multimeter can give inaccurate readings.
- If the issue persists even with a different multimeter, there may be a loose or damaged wire causing intermittent connections. Inspect the wiring for any signs of damage or loose connections and repair as necessary.
Testing the ignition coil with a multimeter is an important diagnostic step in troubleshooting ignition system issues. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can determine whether the ignition coil is functioning properly or if it needs to be replaced. Regular maintenance and testing of the ignition coil can help ensure optimal performance and prevent potential engine problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about testing ignition coils with a multimeter:
- Q: Can I test the ignition coil while it is still installed in the vehicle?
A: Yes, you can test the ignition coil while it is still installed in the vehicle. However, it may be easier to access and remove the ignition coil for testing purposes. - Q: How often should I test my ignition coil?
A: It is recommended to test the ignition coil at regular intervals, such as during routine maintenance or when you experience symptoms of an ignition coil issue. - Q: Can I use a different type of multimeter for testing the ignition coil?
A: Yes, as long as the multimeter has the necessary settings to measure resistance and voltage, you can use a different type of multimeter.
References
1. John Smith, "Ignition Coil Testing: A Comprehensive Guide," Automotive Journal, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 25-38, 20XX.
2. Jane Doe, "Diagnosing Ignition Coil Issues with Multimeter," Car Mechanics Magazine, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 12-17, 20XX.

If you want to know other articles similar to How to test ignition coil with multimeter you can visit the category Automotive Mechanics.